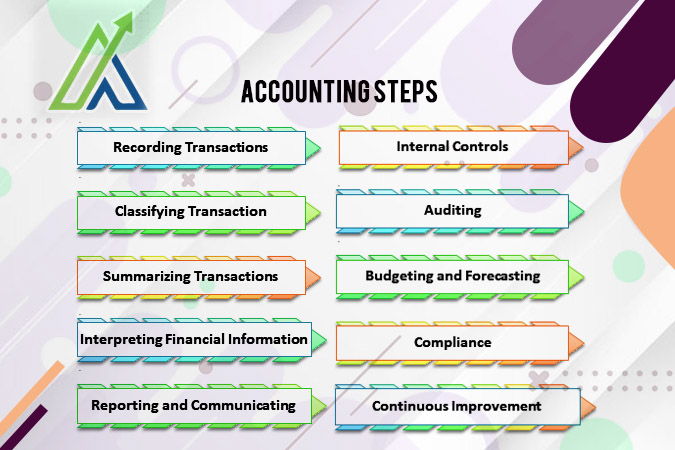
Process of Accounting
The accounting process involves several essential steps:
- Recording Transactions
This initial step involves recording financial transactions systematically. Utilizing the double-entry method ensures that for every debit entry, there is an equal and corresponding credit entry, maintaining the accounting equation’s balance.
- Classifying Transactions
Next step is the categorization of transactions. Transactions are categorized into specific accounts, including assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. This classification provides a structured framework for organizing financial data.
- Summarizing Transactions
The classified transactions are then aggregated and summarized to generate key financial statements such as the income statement and balance sheet. This step provides a comprehensive overview of the company’s financial performance and position.
- Interpreting Financial Information
Financial statements are analyzed to extract insights into the business’s financial health, performance, and overall position. This analysis aids decision-making and strategic planning.
- Reporting and Communicating
Financial reports are prepared and presented to stakeholders, including management, investors, and regulatory authorities. Effective communication of financial information is crucial for transparency and accountability.
- Internal Controls
Implementation of internal controls is essential to safeguard assets, prevent fraud, and ensure the accuracy of financial information. This step contributes to the reliability and integrity of the accounting process.
- Auditing
Periodic audits, whether conducted internally or externally, verify the accuracy and reliability of financial records. Auditing enhances confidence in the financial statements and ensures compliance with accounting standards.
- Budgeting and Forecasting
Planning for future financial activities involves budgeting and forecasting. These tools guide decision-making by projecting expected revenues, expenses, and overall financial performance.
- Compliance
Adherence to legal and regulatory requirements, including accounting standards and tax regulations, is crucial. Compliance ensures that the business operates within the legal framework, avoiding penalties and legal issues.
- Continuous Improvement
Regular assessment and enhancement of accounting processes are undertaken for efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability to changing business needs. Continuous improvement ensures that the accounting system evolves with the company’s growth and dynamic business environment.
This cyclical and systematic process enables businesses to maintain precise financial records, make informed decisions, and fulfill legal and regulatory obligations effectively.